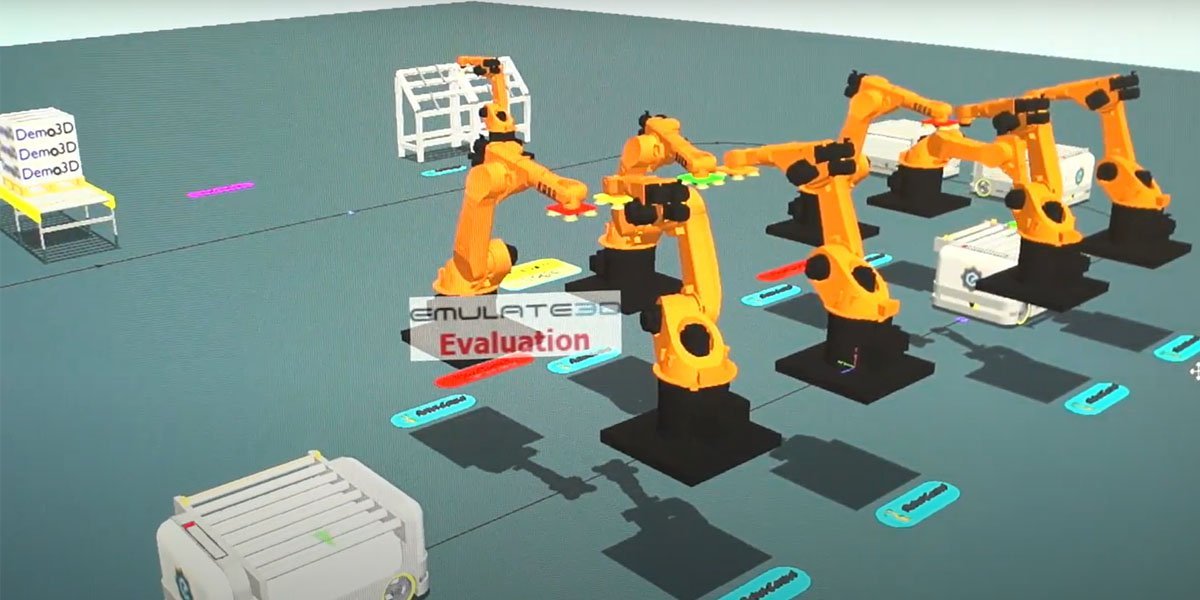
Digital Simulation – A Forward Thinking Asset
One of Applied Integration’s main growth areas is creating simulation models or ‘digital twins’. There are three main stages when it comes to digital simulation/digital twins; Demonstration, System Simulation and System Emulation.
Garry Lofthouse, CEO of Applied Integration explains, “When one of our clients is wanting to build a machine, a process line or a new car, we design everything using software called Emulate 3D and we simulate what they are going to be making before they commit any money to the production of whatever it is they want to build. By building a digital model and simulating the process of the build, we can determine if their process is going to work before they commit to the build”.
Typical Applications/Markets of Digital Simulation
Car Manufacture
Baggage Handling Systems
Conveyors
Cranes
Robots
Food and Drink Processing
Automated Forklift Truck
Digital simulation allows our clients to visually conceptualise the feasibility of their designs. The emulation stage then allows clients to test coding before it is applied to the real system. “Using digital technology, we can highlight areas of concern before any building takes place,” Garry says. “If a production line is going to have a throughput of a trillion items a year, we can map and model it to see if it can manage that throughput, before anything is actually built. Emulation allows you to do all the testing and interaction in a simulated world while the model is being built. The result: you get a more reliable product at the end of it. You do things with the software you would never do with a real live system to push it to the limit.”
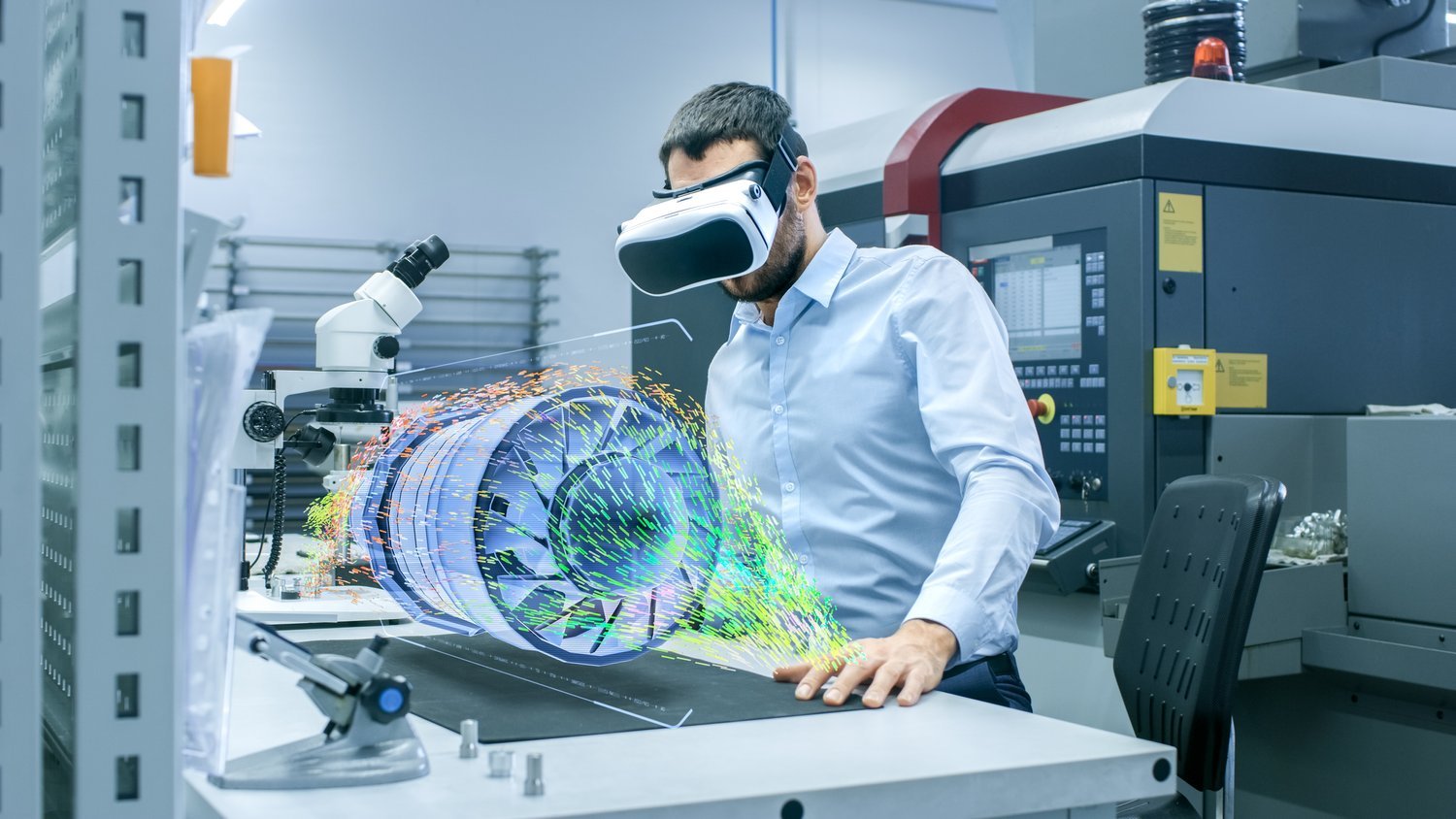
Augmented reality enables the client to use a tablet with the correct software on it and move it over a piece of equipment to get all the details of what’s happening with that equipment, such as its performance levels. Virtual reality also enables clients to take their product or process into a multitude of environments.
So what benefits are there to you?
Emulate 3D Controls simplifies control logic testing. Simulation helps reduce the risk associated with project decisions by clearly demonstrating the consequences of system design choices. It allows the company to make better decisions based on repeatable simulation analysis and produce better outcomes. By using a 3D model to provide realistic feedback in place of the real automated system, operator training becomes safer, cheaper, and does not disrupt existing production. Simulation also helps to shorten the project's critical path with virtual commissioning and reduce overall testing time.
Applied Integration have ten years of experience in system validation and testing, virtual commissioning and digital twin creation using Emulate3D. We have demonstrated validation and testing of system designs using simulation models of the system, running for extended periods. We have incorporated failure scenarios by returning data from salient points which highlights any performance issues.
Emulate3D models can be viewed, explored, and discussed using a variety of new systems that fall into two main categories: Augmented Reality (AR), and Virtual Reality (VR). These can be used in all markets.
VR systems immerse users in a computer-generated world where they can navigate and interact, viewing complex operations in a clear and convincing way. In VR systems which can connect to live models, this level of interaction can alter the way the modelled system behaves, either through browser-based HMIs, or through buttons and levers, all of which enhance the feeling of really "being there". Smartphone-based VR systems can show recordings of operating models but nonetheless include more features than video, as the camera position within the model can be altered by the user.
AR systems incorporate models into the real world by locating them precisely with respect to the real environment, giving the impression of solidity as viewers move around them. Because AR systems include the real environment, they offer great possibilities for demonstrating new solutions to others - including remotely. Several viewers can move around, see each other as avatars, and interact with the running model, while the dialogue between them continues.
With Virtual Reality, we can place a customer or operator within the model to explain or train the individual on the operation of the system. With Augmented Reality, we can place the system as an overlay on a device (headset, tablet), for instance an operator on site could point a device at a machine within a system and have information on its current state (relayed from a virtual twin). VR also assists with major CO2 reductions across companies.
Applied Integration (AI) is a leading systems integrator, specialising in delivering the latest industry technologies with a focus on Industry 4.0, Digitalisation, Internet of Things (IoT), Analytics, Big data / Cloud Technologies, Safety Critical Systems (SIL1, SIL2, SIL3) and Robotics and Collaborative Robots (Cobots). Founded in 2005, AI has grown by being innovative in their approach to providing solutions for the industries we deal with. We have a dynamic, 46 strong engineering team with many years combined experience.